Women's Property Rights in India: Laws, Challenges & Reforms
Updated on : 24 March 2025

Image Source: Google.com
Overview
Women's property rights in India have improved with laws like the Hindu Succession (Amendment) Act, 2005, ensuring equal inheritance. However, challenges like patriarchy, legal delays, and social stigma persist. This blog covers key laws, inheritance rights, challenges, and landmark judgments.

Image Source: google.com
Property rights for women as a mother
| Aspect | Rights of a Mother |
|---|---|
| Legal Heir | Under the Hindu Succession Act, 1956, mothers are Class I heirs. |
| Inheritance Rights | Mothers inherit property if a male or female owner dies, along with spouse and children. |
| Equal Distribution | Even without a Will, assets are distributed fairly, including to married daughters. |
| Property Disposal | Mothers have the right to dispose of their property as they wish, ensuring no disputes. |
| Widowed Mother’s Rights | A widowed mother is entitled to an equal share of her son's property in a joint family. |
Explore Properties in Delhi
- Builder Floors for Sale in New Ashok Nagar
- Builder Floors for Sale in Chhatarpur
- Builder Floors for Sale in Molar Band
- Builder Floors for Sale in Hari Nagar
- Builder Floors for Sale in Vikas Puri
- Builder Floors for Sale in Uttam Nagar
Property rights for women as a daughter
Daughters have equal inheritance, residence, and disposal rights.
| Aspect | Rights of a Daughter |
|---|---|
| Equal Inheritance | Daughters inherit equally from both parents' property. |
| No Gender Discrimination | Laws ensure no discrimination in property rights. |
| Liabilities | Daughters share equal financial liabilities as sons. |
| Right to Residence | Daughters can reside in parental homes, regardless of status. |
| Property Disposal | They can sell, gift, or Will their inherited assets. |
You Might Also Like
Property rights for women as a wife
A married woman has full rights over inherited, owned, and gifted property.
| Aspect | Rights of a Married Woman |
|---|---|
| Husband’s Property | She inherits all assets earned, gifted, or Willed to her. |
| Parental Property | She can claim ownership under the 2005 amendment. |
| Property Disposal | She can sell, gift, or transfer her property freely. |
| Right to Residence | She has the right to maintenance and shelter. |
| Inheritance & Partition | She gets an equal share in inheritance and partition. |
Looking for Plots in India? 🏡✨ Find your perfect plot on HexaHome! 🔑🏠
Property rights for women as a re-married woman
A re-married widow retains inheritance rights, but divorced women do not
| Aspect | Rights of a Re-married Woman |
|---|---|
| Polygamy | Illegal under the Hindu Marriage Act, 1955. |
| Widow’s Rights | She inherits her first husband's property as a Class I heir. |
| Divorce & Property | A divorced woman loses claim to her first husband's assets. |
| Informal Separation | She has no claim on her second husband's property. |
| Inheritance | A second husband’s property goes to his children or parents. |
Steps taken to address property rights for women in India
✅ 2005 Amendment: Gave daughters equal coparcenary rights in ancestral property.
✅ Supreme Court Ruling: Rights apply by birth, even if the father died before 2005.
✅ Marriage Impact: A daughter’s marital status does not affect inheritance rights.
✅ Section 14, HSA 1956: Women are absolute owners of their property, not limited owners.
These steps ensure equal inheritance and financial independence for women. 🚀
🏡 Don't miss out! Find your commercial property on HexaHome! 🔥
Property rights for women Latest judgements
✅ Madras High Court (Sep 2023): Recognized homemakers' contributions as equal, granting them asset entitlement even if bought by the husband.
✅ Calcutta High Court: Clarified that a property bought by a husband in his wife’s name is not always a Benami transaction, stressing intent matters.
✅ Impact: These rulings strengthen women's property rights, but awareness remains low. Families must acknowledge women’s equal inheritance rights. 🚀
Looking for Rent in India? 🏡✨ Find your perfect rental on HexaHome! 🔑🏠
Challenges and Barriers to Women's Property Rights
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Lack of Awareness | Many women are unaware of their legal property rights. |
| Social & Cultural Barriers | Patriarchal norms often prevent women from claiming inheritance. |
| Legal Complexities | Lengthy legal processes discourage women from asserting rights. |
| Family Opposition | Pressure from family members restricts women from claiming property. |
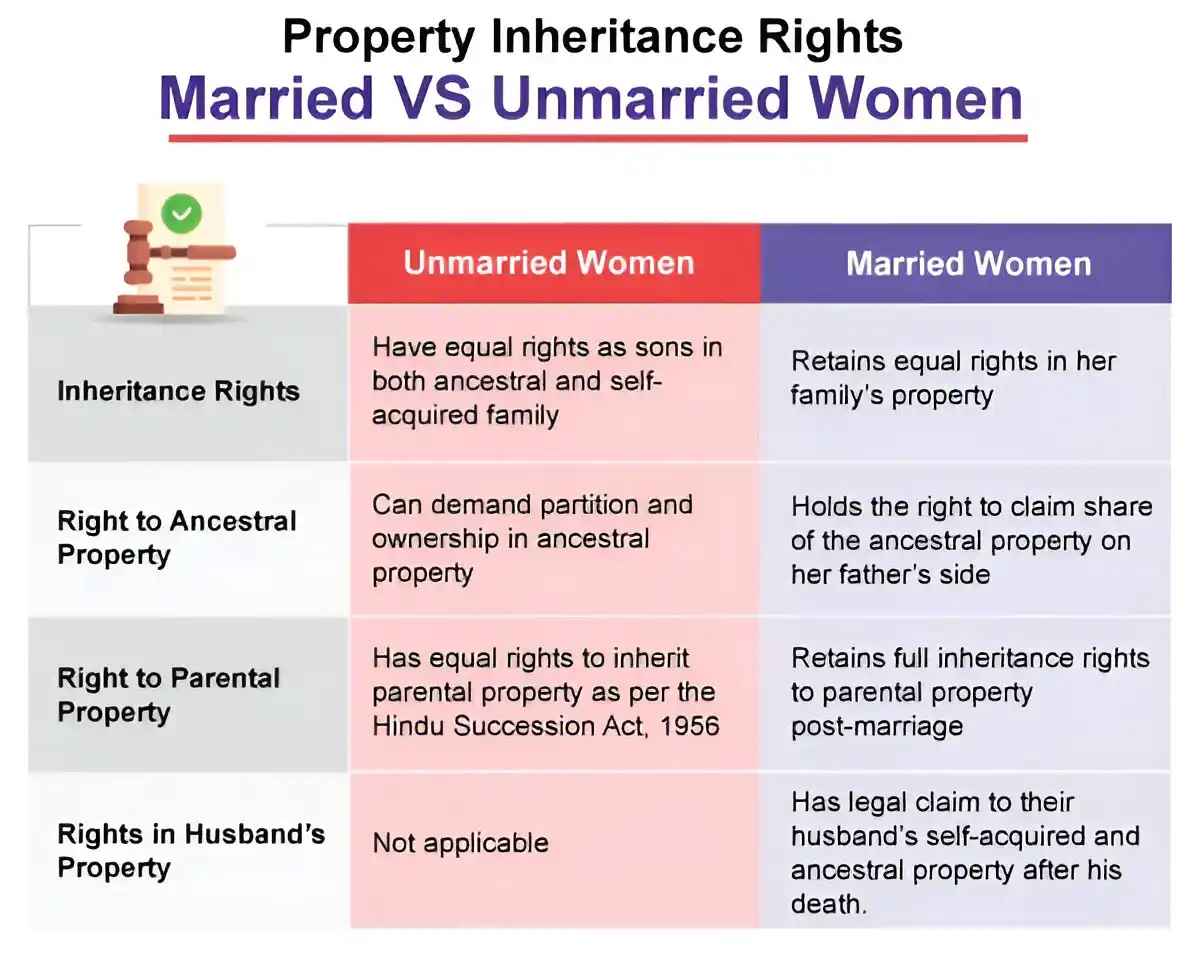
Image Source: google.com
Recent Legal Developments and Landmark Judgments
✅ 2005 Amendment: Gave daughters equal inheritance rights in ancestral property.
✅ Supreme Court: Declared daughters coparceners by birth, regardless of the father’s death.
✅ Madras HC (2023): Recognized homemakers' contributions, granting them asset rights.
✅ Calcutta HC: Stated not all properties in a wife’s name are Benami, intent matters.
✅ Impact: Legal reforms strengthen women’s rights, but awareness is crucial. 🚀
Explore Properties in Delhi
- Builder Floors for Sale in New Ashok Nagar
- Builder Floors for Sale in Chhatarpur
- Builder Floors for Sale in Molar Band
- Builder Floors for Sale in Hari Nagar
- Builder Floors for Sale in Vikas Puri
- Builder Floors for Sale in Uttam Nagar
FAQs
Que: Do daughters have equal rights in ancestral property?
Ans: Yes, the 2005 amendment grants daughters the same inheritance rights as sons.
Que: Can a married woman inherit her parents' property?
Ans: Yes, marriage does not affect her right to parental inheritance.
Que: Does a widow inherit her husband's property?
Ans: Yes, a widow is a Class I heir to her late husband's assets.
Que: Do homemakers have rights to their husband's property?
Ans: Yes, courts recognize homemakers’ contributions, granting them asset rights.
Que: Is a property in a wife’s name always a Benami transaction?
Ans: No, courts rule intent matters before labeling it Benami.
India's Best Real Estate Housing App
Scan to Download the app

Explore Properties for Sale in Delhi:
- Builder Floors for Sale in New Ashok Nagar Delhi
- Builder Floors for Sale in Chhatarpur Delhi
- Builder Floors for Sale in Molar Band Delhi
- Builder Floors for Sale in Hari Nagar Delhi
- Builder Floors for Sale in Vikas Puri Delhi
- Builder Floors for Sale in Uttam Nagar Delhi
- Apartments for Sale in Vasant Kunj Delhi
- Apartments for Sale in Kalkaji Delhi
- Apartments for Sale in Chandan Hola Delhi
- Apartments for Sale in Uttam Nagar Delhi
- Apartments for Sale in Chhatarpur Delhi
- House for Sale in Uttam Nagar Delhi
- House for Sale in Jharoda Kalan Delhi
- Retail Shop for Sale in Narela Delhi
Explore Properties for Rent in Delhi:
- Apartments for Rent in Saket Delhi
- Apartments for Rent in Lajpat Nagar Delhi
- Apartments for Rent in Vasant Kunj Delhi
- Apartments for Rent in Greater Kailash Delhi
- Apartments for Rent in Chhattarpur Enclave Phase I Delhi
- Apartments for Rent in Malviya Nagar Delhi
- Apartments for Rent in Chhatarpur Delhi
- Apartments for Rent in Chittaranjan Park Delhi
- Apartments for Rent in Kalkaji Delhi
- Apartments for Rent in Neb Sarai Delhi
- Builder Floors for Rent in Saket Delhi
- Builder Floors for Rent in Chhatarpur Delhi
- Builder Floors for Rent in Paschim Vihar Delhi
- Builder Floors for Rent in Neb Sarai Delhi
- Builder Floors for Rent in Mukherjee Nagar Delhi
- 1 Rk Studio for Rent in Mukherjee Nagar Delhi
- 1 Rk Studio for Rent in Mayur Vihar Phase 1 Delhi
- 1 Rk Studio for Rent in Guru Teg Bahadur Nagar Delhi
- Office Space for Rent in Saket Delhi
- Office Space for Rent in Janakpuri Delhi
- Office Space for Rent in Patel Nagar Delhi
- House for Rent in Laxmi Nagar Delhi
- House for Rent in Todapur Delhi
Explore PG’s for Rent in Delhi:
- PG’s for Rent in Dwarka Delhi
- PG’s for Rent in Karol Bagh Delhi
- PG’s for Rent in Saket Delhi
- PG’s for Rent in Greater Kailash Delhi
- PG’s for Rent in Kalkaji Delhi
- PG’s for Rent in Hari Nagar Ashram Delhi
- PG’s for Rent in Vikas Puri Delhi
- PG’s for Rent in New Mahavir Nagar Delhi
- PG’s for Rent in Gujranwala Town Delhi
- PG’s for Rent in Kotla Mubarakpur Delhi
Explore Co-living options in Delhi:
- Sharing Room/Flats in Saket Delhi
- Sharing Room/Flats in Kalkaji Delhi
- Sharing Room/Flats in Chhatarpur Delhi
- Sharing Room/Flats in Safdarjung Enclave Delhi
- Sharing Room/Flats in Guru Teg Bahadur Nagar Delhi
- Sharing Room/Flats in Chittaranjan Park Delhi
- Sharing Room/Flats in Vasant Kunj Delhi
- Sharing Room/Flats in South Ex 2 Delhi
- Sharing Room/Flats in East of Kailash Delhi
- Sharing Room/Flats in Sheikh Sarai Delhi
- Sharing Room/Flats in Rohini Delhi
- Sharing Room/Flats in East of Kailash Delhi
- Sharing Room/Flats in Greater Kailash Delhi
- Sharing Room/Flats in Saket Delhi
- Sharing Room/Flats in Kalkaji Delhi
Buy, Sell & Rent Properties – Download HexaHome App Now!
Find your perfect home, PG, or rental in just a few clicks.
Post your property at ₹0 cost and get genuine buyers & tenants fast
Smart alerts & search helps you find homes that fit your budget.
Available on iOS & Android
A Product By Hexadecimal Software Pvt. Ltd.